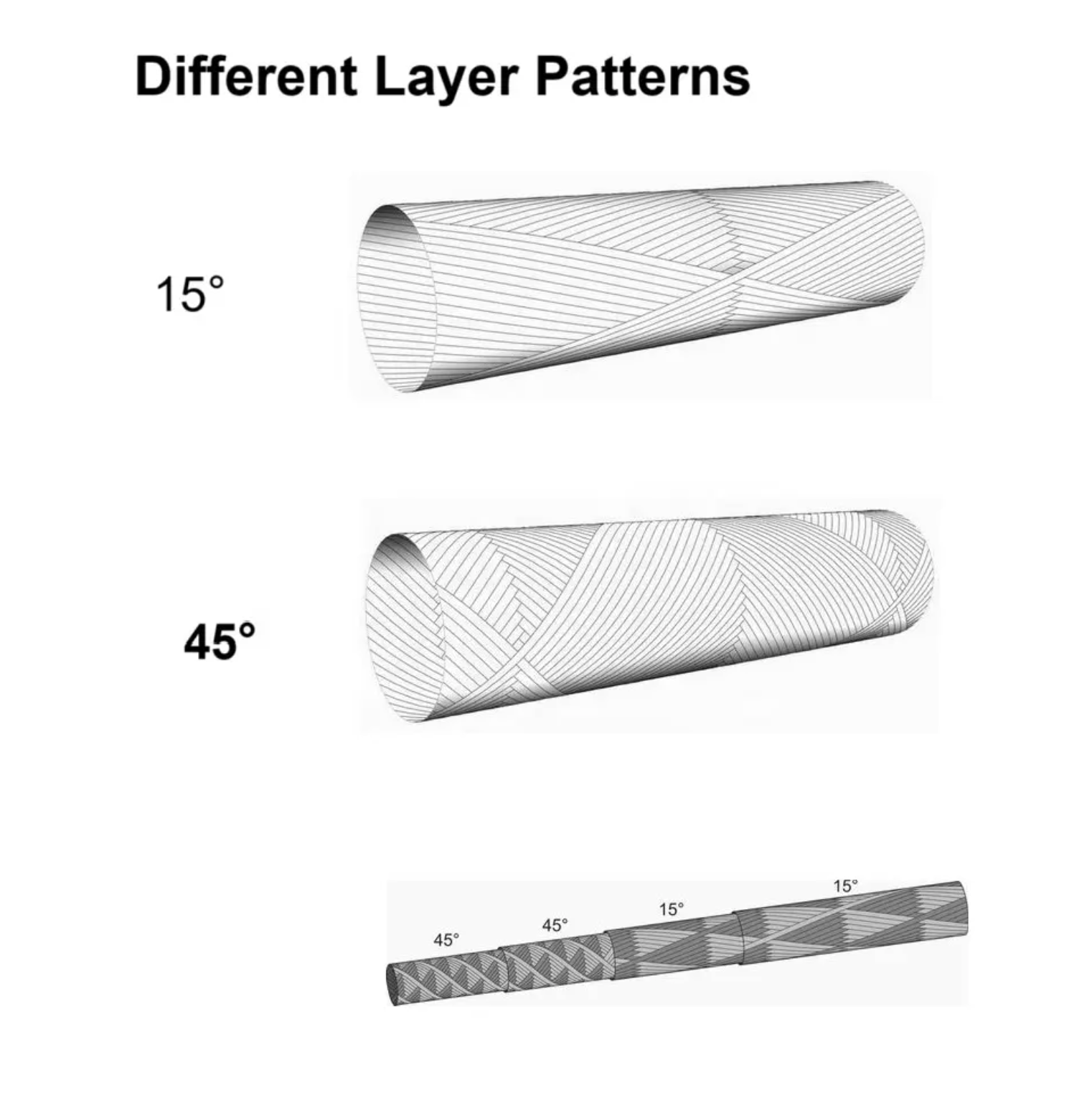
Filament winding is a precise manufacturing process used to produce high-performance carbon fiber tubes. One of the key factors affecting the mechanical properties of these tubes is the filament winding angle, which refers to the orientation of carbon fiber strands relative to the tube’s axis. The selection of winding angles is critical as it directly impacts the tube’s strength, stiffness, and overall performance in various applications.
Common Filament Winding Angles and Their Effects
Filament winding angles typically range from 0° to 90°, with different angles serving specific structural purposes:
- Low Angles (0° – 30°): Axial Strength and Stiffness
Tubes wound at low angles have fibers aligned closer to the axial direction, providing superior tensile and compressive strength along the length of the tube. These are ideal for applications requiring high axial load resistance, such as aerospace structures, robotics arms, and lightweight mechanical components. - Medium Angles (30° – 60°): Balanced Performance
Medium-angle windings offer a balance between axial and hoop strength, making them suitable for applications that require resistance to both longitudinal and radial forces. These tubes are often used in sports equipment, industrial rollers, and automotive drive shafts. - High Angles (60° – 90°): Hoop Strength and Pressure Resistance
High-angle winding results in fibers being oriented more perpendicularly to the tube’s axis, providing enhanced hoop (radial) strength. This makes the tube highly resistant to internal and external pressures, making them ideal for pressure vessels, fluid transport pipes, and structural supports in marine or oil industries.
Optimizing Winding Angles for Specific Applications
Engineers often customize winding patterns by combining multiple angles to achieve the desired balance of strength, stiffness, and weight. For example:
- Hybrid Layups: A combination of 0°, 45°, and 90° angles is used to enhance multi-directional strength.
- Customized Layups: Depending on load conditions, specific angles can be adjusted to optimize the tube’s performance under tensile, compressive, or bending stresses.
Conclusion
Filament winding angles play a crucial role in determining the mechanical properties of carbon fiber tubes. By selecting the appropriate angle or combination of angles, manufacturers can tailor tube performance to meet specific industry demands. Whether for aerospace, automotive, or industrial applications, understanding and optimizing winding angles is essential for producing high-strength, lightweight, and durable carbon fiber components.






